Understanding cut-resistant levels is crucial for selecting the right protective gloves. These levels are standardized to measure a glove’s ability to withstand cuts from sharp objects.
Cut-resistant levels, determined by EU and ANSI standards, classify gloves from low to high protection based on testing methods and scores.
In this article, we’ll explore EU and ANSI cut-resistant levels, their application in Canada, and OSHA requirements for workplace safety.
What are EU cut resistant levels?
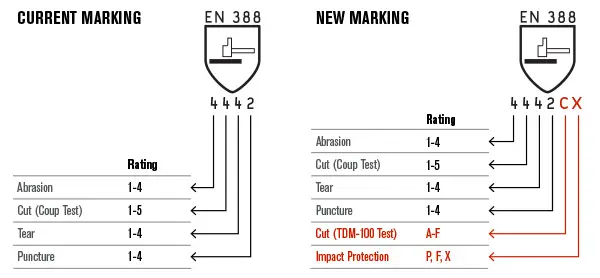
The European Union (EU) has established the EN388 standard to classify gloves based on their resistance to mechanical hazards, including cuts. EN388 is widely recognized across Europe and in many other markets, offering a reliable benchmark for assessing glove safety.
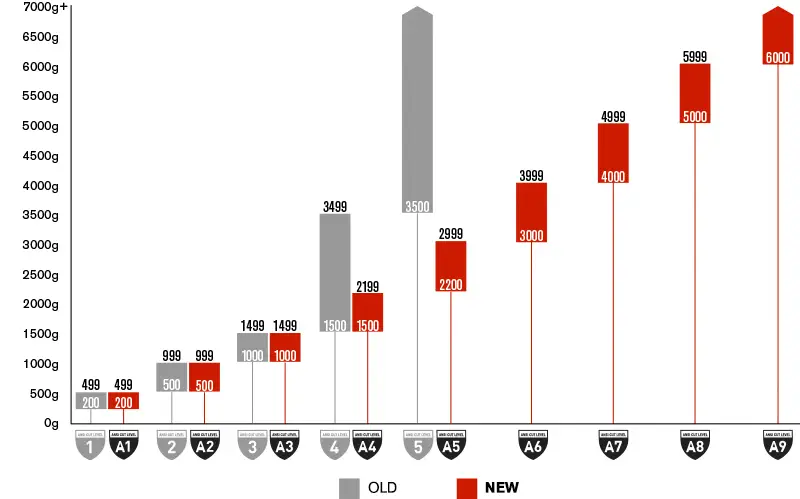
EU cut-resistant levels range from 1 to 5, with higher levels indicating greater resistance to cuts.
How EN388 Levels Are Determined
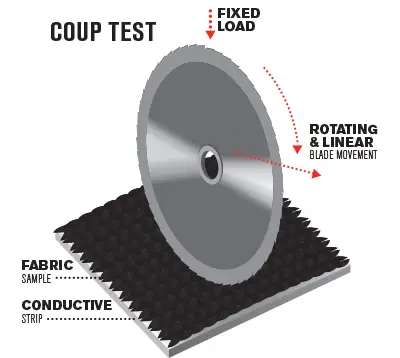
The EN388 standard uses a "Coupe Test" to measure a glove’s cut resistance. In this test, a rotating circular blade applies force to the glove material, and the number of cycles it takes to cut through the material determines the cut level.
| Level | Blade Cycles (Coupe Test) | Cut Resistance (N) | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | 1.2 to 2.4 | Low | Light handling, general work |
| Level 2 | 2.5 to 5.0 | Moderate | Packaging, light assembly |
| Level 3 | 5.1 to 10.0 | High | Automotive, manufacturing |
| Level 4 | 10.1 to 15.0 | Very High | Metal handling, construction |
| Level 5 | 15.1+ | Maximum | Heavy-duty cutting tasks |
Limitations of EN388
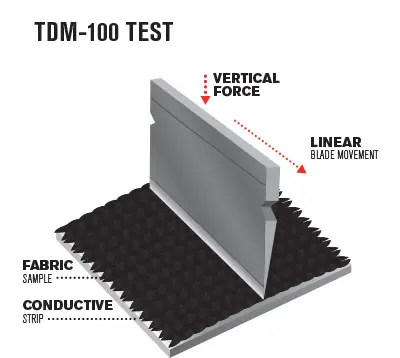
- Coupe Test vs. TDM Test: The Coupe Test may not accurately measure resistance to certain materials like serrated blades. To address this, the ISO 13997 (TDM) test measures the force needed to cut the glove.
- Aging of Materials: Some gloves lose their effectiveness over time due to wear and environmental exposure.
Additional Considerations
While EN388 is reliable, it’s essential to match the glove’s cut level to the specific hazards in your workplace. For example, gloves with Level 5 protection are ideal for industries like metalworking, while Level 1 gloves may suffice for basic warehouse tasks.
Understanding these ratings ensures you choose gloves that offer the right balance of safety and functionality.
What are ANSI cut resistant levels?

The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) provides another widely recognized method for assessing cut resistance. The ANSI/ISEA 105 standard measures the amount of weight (in grams) required to cut through glove material using a straight blade.
ANSI cut levels range from A1 to A9, offering a broader classification compared to EN388 standards.
ANSI Cut Level Ratings
| Level | Force (grams) | Protection Level | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 200 to 499 | Low | Light packaging, basic tasks |
| A2 | 500 to 999 | Moderate | General assembly, light-duty work |
| A3 | 1,000 to 1,499 | High | Glass handling, automotive |
| A4 | 1,500 to 2,199 | Very High | Metal stamping, sharp tools |
| A5 | 2,200 to 2,999 | Superior | Heavy manufacturing |
| A6 | 3,000 to 3,999 | Exceptional | Steel cutting, high-risk jobs |
| A7 | 4,000 to 4,999 | Extreme | Industrial glass, mining |
| A8 | 5,000 to 5,999 | Maximum | Precision metalwork |
| A9 | 6,000+ | Ultimate | Extreme cutting environments |
Benefits of ANSI Standards
- Real-World Accuracy: ANSI testing simulates real cutting tasks, offering better insights into glove performance.
- Broad Spectrum: With nine levels, ANSI provides more precise classification, making it easier to match gloves to specific tasks.
Key Differences Between ANSI and EN388
| Aspect | ANSI | EN388 |
|---|---|---|
| Testing Method | Measures cutting force | Measures blade cycles |
| Cut Levels | A1 to A9 | Levels 1 to 5 |
| Focus | Real-world applications | Mechanical hazard testing |
ANSI standards are particularly popular in North America, making them ideal for industries with high safety requirements.
Does ANSI cut resistant levels can be used in Canada?
Canada often aligns its safety standards with global practices, including those from the U.S. As such, ANSI cut-resistant levels are commonly recognized and applied in Canadian workplaces.
Yes, ANSI cut-resistant levels are widely accepted in Canada, ensuring compliance with workplace safety regulations.
Why ANSI Levels Work in Canada
- Alignment with CSA Standards: The Canadian Standards Association often incorporates ANSI/ISEA testing methods, ensuring consistency across North America.
- Regulatory Compliance: Industries such as manufacturing and construction frequently rely on ANSI-rated gloves to meet safety requirements.
- Global Trade: Many Canadian companies import gloves from ANSI-compliant manufacturers, simplifying logistics and ensuring quality.
Common Applications of ANSI Standards in Canada
| Industry | Typical Hazards | ANSI Levels Used |
|---|---|---|
| Construction | Sharp tools, glass | A4 to A6 |
| Manufacturing | Metals, machinery | A5 to A7 |
| Mining | Abrasive and cutting tools | A6 to A9 |
| Oil and Gas | Rigging, sharp edges | A4 to A6 |
By choosing ANSI-rated gloves, Canadian employers can ensure high safety standards and compatibility with local regulations.
Does OSHA require cut resistant gloves?
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) emphasizes workplace safety, including hand protection. However, OSHA does not mandate specific cut-resistant gloves.
OSHA requires employers to assess hazards and provide appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including cut-resistant gloves if necessary.
OSHA’s Hand Protection Requirements
- Hazard Assessment: Employers must evaluate risks like sharp edges, heavy machinery, and abrasive materials.
- PPE Selection: Gloves should match the identified hazards. For example, ANSI or EN388-rated gloves are often suitable.
- Employee Training: Workers must understand how to use and maintain gloves properly.
Examples of OSHA Compliance
| Industry | Common Hazards | Required Gloves |
|---|---|---|
| Metalworking | Sharp edges, heat | ANSI A4 or higher |
| Construction | Glass, metal, tools | EN388 Level 4 or ANSI A5 |
| Food Processing | Blades, sharp tools | ANSI A3 to A5, food-safe materials |
By complying with OSHA’s guidelines, businesses can ensure worker safety and avoid legal penalties.
Conclusion
Cut-resistant levels, defined by ANSI and EN388 standards, provide crucial guidance for selecting the right gloves. Understanding these levels ensures safety, compliance, and efficiency in any workplace.



